茶多酚抗肥胖的研究进展
摘要: 肥胖是糖尿病、心血管疾病、肿瘤等若干慢性疾病的主要风险因素和病理基础,目前已成为全球公共卫生健康问题之一。随着肥胖率的增高,对于天然抗肥胖药物的研究和应用已经成为人们持续关注的热点。茶多酚(Tea Polyphenols,TP)是茶叶中多酚类物质的总称,在茶叶中含量丰富、功效显著,大量研究表明其在抗肥胖方面具有良好的效果,发展前景广。本文围绕茶多酚抗肥胖,综述了近年来在体外,动物和临床研究中的研究进展,并分别从茶多酚调节肠道菌群的结构和组成,调节炎症反应,促进能量消耗,调控相关酶的活性并抑制脂类的合成和吸收等途径探讨防治肥胖的机制,以期为开发含天然茶多酚的减肥食品或药物奠定基础。
关键词: 肥胖 / 茶多酚 / 肠道菌群 / 炎症反应 / 能量代谢Abstract: Obesity is a major risk factor and pathological basis for several chronic diseases such as diabetes, cardiovascular diseases, and tumors. It has now become a global public health issue. With the increasing prevalence of obesity, research and application of natural anti-obesity drugs have become a continuous focus of attention. Tea polyphenols (TP), collectively known as polyphenolic substances in tea, are abundant and significant in their effects in tea. Numerous studies have shown that tea polyphenols have good anti-obesity effects and promising prospects. This article reviews the research progress on tea polyphenols and their anti-obesity effects in recent years, focusing on in vitro, animal, and clinical studies. It discusses the mechanisms of preventing and treating obesity through tea polyphenols, including the regulation of intestinal microbiota composition, modulation of inflammatory response, promotion of energy expenditure, regulation of enzyme activity, and inhibition of lipid synthesis and absorption. The aim is to lay a foundation for the development of natural tea polyphenol-based weight-loss foods or drugs.
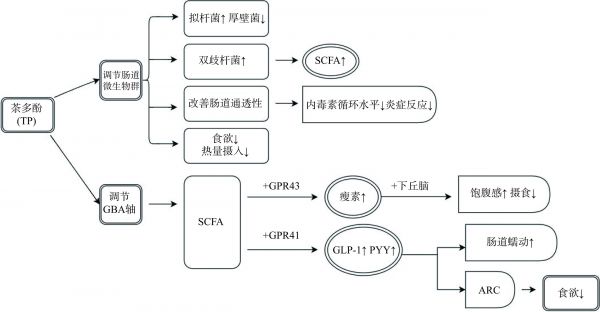
图 1 茶多酚通过调节肠道菌群的结构和组成防治肥胖的作用机制图
注:GBA:肠脑轴;SCFA:短链脂肪酸;GPR43:G蛋白偶联受体43;GPR41:G蛋白偶联受体41;GLP-1:胰高血糖素样肽-1;PYY:肽YY;ARC:下丘脑弓状核。
Figure 1. Tea polyphenols prevent and treat obesity by modulating the structure and composition of the intestinal microbiota
[1]ZHANG X, HA S, LAU H C, et al. Excess body weight:Novel insights into its roles in obesity comorbidities[J]. Seminars in Cancer Biology,2023,92:16−27. doi: 10.1016/j.semcancer.2023.03.008
[2] 中国营养学会肥胖防控分会, 中国营养学会临床营养分会, 中华预防医学会行为健康分会, 等. 中国居民肥胖防治专家共识[J]. 西安交通大学学报(医学版),2022,43(4):619−631. [Chinese Nutrition Society Obesity Prevention and Control Section, Chinese Nutrition Society Clinical Nutrition Section, Chinese Preventive Medicine Association Behavioral Health Section, et al. Expert consensus on obesity prevention and treatment in China[J]. Journal of Xi'an Jiaotong University (Medical Sciences),2022,43(4):619−631.]Chinese Nutrition Society Obesity Prevention and Control Section, Chinese Nutrition Society Clinical Nutrition Section, Chinese Preventive Medicine Association Behavioral Health Section, et al. Expert consensus on obesity prevention and treatment in China[J]. Journal of Xi'an Jiaotong University (Medical Sciences), 2022, 43(4): 619−631.
[3]LI Z, ZHANG B, WANG N, et al. A novel peptide protects against diet-induced obesity by suppressing appetite and modulating the gut microbiota[J]. Gut, 2022, 72 (4):686-698.
[4]PERDOMO C M, COHEN R V, SUMITHRAN P, et al. Contemporary medical, device, and surgical therapies for obesity in adults[J]. Lancet,2023,401(10382):1116−1130. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(22)02403-5
[5] 张晓梦, 倪艳, 李先荣. 茶多酚的药理作用研究进展[J]. 药物评价研究,2013,36(2):157−160. [ZHANG Xiaomeng, NI Yan, LI Xianrong. Advances in study on pharmacological effects of tea polyphenol[J]. Drug Evaluation Research,2013,36(2):157−160.]ZHANG Xiaomeng, NI Yan, LI Xianrong. Advances in study on pharmacological effects of tea polyphenol[J]. Drug Evaluation Research, 2013, 36(2): 157−160.
[6]RAJ V, BONKOVSKY H L, AHMAD J, et al. Garcinia cambogia, either alone or in combination with green tea causes moderate to severe liver injury[J]. Clinical Gastroenterology and Hepatology:The Official Clinical Practice Journal of the American Gastroenterological Association,2021,20(6):e1416−e1425.
[7]CABALLERO B. Humans against obesity:Who will win?[J]. Advances in Nutrition,2019,10(Suppl_1):S4−S9.
[8]LONGO M, ZATTERALE F, NADERI J, et al. Adipose tissue dysfunction as determinant of obesity-associated metabolic complications[J]. International Journal of Molecular Sciences,2019,20(9):2358. doi: 10.3390/ijms20092358
[9] 黄书晨, 汪一波. 肥胖发病机制的研究进展[J]. 中国分子心脏病学杂志,2019,19(5):3105−3108. [HUANG Shuchen, WANG Yibo. The progress in the pathogenesis of obesity[J]. Molecular Cardiology of China,2019,19(5):3105−3108.]HUANG Shuchen, WANG Yibo. The progress in the pathogenesis of obesity[J]. Molecular Cardiology of China, 2019, 19(5): 3105−3108.
[10] 徐春花, 何卓俊, 曾立等. 肥胖的发病机制以及药物治疗研究概况[J]. 中国疗养医学,2021,30(2):131−135. [XU Chunhua, HE Zhuojun, ZENG Li, et al. Research overview of the pathogenesis of obesity and drug therapy[J]. Chinese Journal of Convalescent Medicine,2021,30(2):131−135.]XU Chunhua, HE Zhuojun, ZENG Li, et al. Research overview of the pathogenesis of obesity and drug therapy[J]. Chinese Journal of Convalescent Medicine, 2021, 30(2): 131−135.
[11]DELAYE M, ROUSSEAU A, MAILLYGIACCHETTI L, et al. Obesity, cancer, and response to immune checkpoint inhibitors:Could the gut microbiota be the mechanistic link?[J]. Pharmacology & Therapeutics,2023,247:108442.
[12] 孙世利, 凌彩金, 刘军, 等. 茶多酚与茶黄素对前脂肪细胞3T3-L1增殖与分化的影响[J]. 广东农业科学,2011,38(12):137−139,213. [SUN Shili, LING Caijin, LIU Jun, et al. Effects of tea polyphenols and theaflavins on proliferation and differentiation of 3T3-L1 preadipocytes[J]. Guangdong Agricultural Sciences,2011,38(12):137−139,213.]SUN Shili, LING Caijin, LIU Jun, et al. Effects of tea polyphenols and theaflavins on proliferation and differentiation of 3T3-L1 preadipocytes[J]. Guangdong Agricultural Sciences, 2011, 38(12): 137−139,213.
[13] 党旭辉, 周秦羽, 刘梦圆, 等. 黑茶金花体外抗氧化及降血脂活性研究[J]. 食品安全质量检测学报,2022,13(24):7927−7933. [DANG Xuhui, ZHOU Qinyu, LIU Mengyuan, et al. Study on antioxidant and hypolipidemic activity in vitro of post-flowering dark tea[J]. Journal of Food Safety & Quality,2022,13(24):7927−7933.]DANG Xuhui, ZHOU Qinyu, LIU Mengyuan, et al. Study on antioxidant and hypolipidemic activity in vitro of post-flowering dark tea[J]. Journal of Food Safety & Quality, 2022, 13(24): 7927−7933.
[14] 李学鸣, 孟宪军, 彭杰. 茶多酚降低小鼠营养性肥胖的效果[J]. 沈阳农业大学学报,2009,40(5):612−615. [LI Xueming, MENG Xianjun, PENG Jie. Studies on weight reducing induced by tea polyphenols in nutritional obese white mouse[J]. Journal of Shenyang Agricultural University,2009,40(5):612−615.]LI Xueming, MENG Xianjun, PENG Jie. Studies on weight reducing induced by tea polyphenols in nutritional obese white mouse[J]. Journal of Shenyang Agricultural University, 2009, 40(5): 612−615.
[15] 田维, 张荣涛, 李悦绮, 等. 绿茶膳食纤维粉对大鼠的减肥降脂作用研究[J]. 粮食与饲料工业,2019(3):49−52. [TIAN Wei, ZHANG Rongtao, LI Yueqi, et al. Effects of green tea fiber powder on weight losing and lipid lowering of rat[J]. Cereal & Feed Industry,2019(3):49−52.]TIAN Wei, ZHANG Rongtao, LI Yueqi, et al. Effects of green tea fiber powder on weight losing and lipid lowering of rat[J]. Cereal & Feed Industry, 2019(3): 49−52.
[16] 夏燕萍, 陈刚, 俞茂华. 茶多酚对实验性肥胖大鼠脂肪组织PPAR-γ表达影响的研究[J]. 中国糖尿病杂志,2012,20(8):625−628. [XIA Yanping, CHEN Gang, YU Maohua. Changes of PPAR-γ expression in adipose tissue of experimental fatty rats after intervention with tea polyphenol[J]. Chinese Journal of Diabetes,2012,20(8):625−628.]XIA Yanping, CHEN Gang, YU Maohua. Changes of PPAR-γ expression in adipose tissue of experimental fatty rats after intervention with tea polyphenol[J]. Chinese Journal of Diabetes, 2012, 20(8): 625−628.
[17]YE J, ZHAO Y, CHEN X M, et al. Puerh tea ameliorates obesity and modulates gut microbiota in high fat diet fed mice[J]. Food Research International,2021,144:110360. doi: 10.1016/j.foodres.2021.110360
[18] 王娟娟. 茶多酚联合有氧体育运动对肥胖少年身体素质的影响[J]. 福建茶叶,2016,38(7):25−26. [WANG Juanjuan. Effects of tea polyphenols combined with aerobic physical exercise on physical fitness of obese adolescents[J]. Tea in Fujian,2016,38(7):25−26.]WANG Juanjuan. Effects of tea polyphenols combined with aerobic physical exercise on physical fitness of obese adolescents[J]. Tea in Fujian, 2016, 38(7): 25−26.
[19]HOSSEINI Z, GHAEDI H, AHMADI M, et al. Lipid-lowering effects of concurrent training and green tea consumption in overweight women[J]. Journal of Obesity & Metabolic Syndrome, 2020, 29(4):313-319.
[20]XIE L Y, TANG Q Y, YAO D, et al. Effect of decaffeinated green tea polyphenols on body fat and precocious puberty in obese girls:A randomized controlled trial[J]. Frontiers in Endocrinology,2021,12:736724. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2021.736724
[21]SUCHODOLSKI J S. Intestinal microbiota of dogs and cats:A bigger world than we thought[J]. Veterinary Clinics of North America:Small Animal Practice,2011,41(2):261−272. doi: 10.1016/j.cvsm.2010.12.006
[22]ZHAO Y, ZHANG X. Interactions of tea polyphenols with intestinal microbiota and their implication for anti-obesity[J]. Journal of the Science of Food and Agriculture,2020,100(3):897−903. doi: 10.1002/jsfa.10049
[23]PÉREZBURILLO S, NAVAJASPORRAS B, LÓPEZMALDONADO A, et al. Green tea and its relation to human gut microbiome[J]. Molecules,2021,26(13):3907. doi: 10.3390/molecules26133907
[24] 张志勇, 李婷, 朱慧芳, 等, 茶多酚调节肠道菌群及抗肥胖作用研究进展[J]. 食品安全质量检测学报, 2023, 14(2):161−167. [ZHANG Zhiyong, LI Ting, ZHU Huifang, et al. Research progress on the regulation of gut microbiota and anti-obesity effect of tea polyphenols[J]. Journal of Food Safety & Quality, 2023, 14(2):161−167.]ZHANG Zhiyong, LI Ting, ZHU Huifang, et al. Research progress on the regulation of gut microbiota and anti-obesity effect of tea polyphenols[J]. Journal of Food Safety & Quality, 2023, 14(2): 161−167.
[25]LIU Z B, CHEN Z C, GUO H W, et al. The modulatory effect of infusions of green tea, oolong tea, and black tea on gut microbiota in high-fat-induced obese mice[J]. Food & Function,2016,7(12):4869−4879.
[26]GUO X, CHENG M, ZHANG X, et al. Green tea polyphenols reduce obesity in high-fat diet-induced mice by modulating intestinal microbiota composition[J]. International Journal of Food Science & Technology,2017,52(8):1723−1730.
[27]SAAD M J A, SANTOS A, PRADA P O. Linking gut microbiota and inflammation to obesity and insulin resistance[J]. Physiology,2016,31(4):283−293. doi: 10.1152/physiol.00041.2015
[28]LIAO Z L, ZENG B H, WANG W, et al. Impact of the consumption of tea polyphenols on early atherosclerotic lesion formation and intestinal bifidobacteria in high-fat-fed Apoe mice[J]. Frontiers in Nutrition,2016,3:42.
[29]CORADO A G, CHRISTIAN H, FELIPE J M. The human gut microbiota:Metabolism and perspective in obesity[J]. Gut microbes,2018,9(4):1−18.
[30]LIU J Y, HE D, XING Y F, et al. Effects of bioactive components of Pu-erh tea on gut microbiomes and health:A review[J]. Food Chemistry,2021,353:129439. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2021.129439
[31]SIROTKIN A V, A K. The anti-obesity and health-promoting effects of tea and coffee[J]. Physiological Research,2021,70(2):161−168.
[32]HOUSER M C, TANSEY, M G. The gut-brain axis:Is intestinal inflammation a silent driver of Parkinson's disease pathogenesis?[J]. NPJ Parkinson's Disease,2017,3(1-2):3.
[33]YAN R N, HO C T, ZHANG X. Interaction between tea polyphenols and intestinal microbiota in host metabolic diseases from the perspective of the gut-brain axis[J]. Molecular Nutrition & Food Research,2020,64(14):e2000187.
[34]CORNEJO-PAREJA I, MUñOZ-GARACH A, CLEMENTE-POSTIGO M, et al. Importance of gut microbiota in obesity[J]. European Journal of Clinical Nutrition,2019,72(Suppl 1):26−37.
[35]LIU X N, LI X, XIA B, et al. High-fiber diet mitigates maternal obesity-induced cognitive and social dysfunction in the offspring via gut-brain axis[J]. Cell Metabolism,2021,33(5):923−938. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2021.02.002
[36]TAYLOR E B. The complex role of adipokines in obesity, inflammation, and autoimmunity[J]. Clinical Science,2021,135(6):731−752. doi: 10.1042/CS20200895
[37] 赵航晔, 夏琛, 何普明, 等. 茶多酚抗炎和促外伤愈合作用及其机制[J]. 浙江大学学报(农业与生命科学版),2021,47(1):118−126. [ZHAO Hangye, XIA Chen, HE Puming, et al. Effects of tea polyphenols on anti-inflammation and promotion of wound healing and its mechanisms[J]. Journal of Zhejiang University (Agriculture and Life Sciences),2021,47(1):118−126.]ZHAO Hangye, XIA Chen, HE Puming, et al. Effects of tea polyphenols on anti-inflammation and promotion of wound healing and its mechanisms[J]. Journal of Zhejiang University (Agriculture and Life Sciences), 2021, 47(1): 118−126.
[38]LI Y, RAHMAN U S, HUANG Y Y, et al. Green tea polyphenols decrease weight gain, ameliorate alteration of gut microbiota, and mitigate intestinal inflammation in canines with high-fat-diet-induced obesity[J]. The Journal of Nutritional Biochemistry,2020,78:108324. doi: 10.1016/j.jnutbio.2019.108324
[39]SAITO M, YUKO O. Thermogenic brown fat in humans:Implications in energy homeostasis, obesity and metabolic disorders[J]. The World Journal of Men's Health, 2023, 41(3):489-507.
[40]L K M, ERIC R. Brown adipose tissue:An update on recent findings[J]. Current Obesity Reports,2017,6(4):389−396. doi: 10.1007/s13679-017-0283-6
[41] 叶小燕, 黄建安, 刘仲华. 茶叶减肥作用及其机理研究进展[J]. 食品科学, 2012, 33(3):308−312. [YE Xiaoyan, HUANG Jianan, LIU Zhonghua, Anti-obesity effect and mechanism of tea:A review[J]. Food Science, 2012, 33(3):308−312.]YE Xiaoyan, HUANG Jianan, LIU Zhonghua, Anti-obesity effect and mechanism of tea: A review[J]. Food Science, 2012, 33(3): 308−312.
[42]LIU T T, LIU X T, CHEN Q X, et al. Lipase inhibitors for obesity:A review[J]. Biomedicine & Pharmacotherapy,2020,128:110314.
[43]WANG S, MOUSTAID-MOUSSA N, CHEN L, et al. Novel insights of dietary polyphenols and obesity[J]. The Journal of Nutritional Biochemistry,2014,25(1):1−18. doi: 10.1016/j.jnutbio.2013.09.001
[44]SUN N N, WU T Y, CHAU C F. Natural dietary and herbal products in anti-obesity treatment[J]. Molecules,2016,21(10):1351. doi: 10.3390/molecules21101351
[45] 张忠. 茶多酚对胰脂肪酶活性的抑制作用[J]. 食品工业,2013,34(8):168−170. [ZHANG Zhong. The inhibition of tea polyphenol on pancreatic lipase[J]. The Food Industry,2013,34(8):168−170.]ZHANG Zhong. The inhibition of tea polyphenol on pancreatic lipase[J]. The Food Industry, 2013, 34(8): 168−170.
[46] 周永强, 周维, 岳兰昕, 等. 雷公藤红素参与脂质代谢调控的研究进展[J]. 医药导报,2021,40(12):1704−1709. [ZHOU Yongqiang, ZHOU Wei, YUE Lanxin, et al. Research progress on the role of celastrol in the regulation of lipid metabolism[J]. Herald of Medicine,2021,40(12):1704−1709.]ZHOU Yongqiang, ZHOU Wei, YUE Lanxin, et al. Research progress on the role of celastrol in the regulation of lipid metabolism[J]. Herald of Medicine, 2021, 40(12): 1704−1709.
[47]ABUNOFAL O, MOHAN C. Salubrious effects of green tea catechins on fatty liver disease:A systematic review[J]. Medicines,2022,9(3):20. doi: 10.3390/medicines9030020
[48]NAGASHIMADA M, OTA T. Role of vitamin E in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease[J]. Iubmb Life,2019,71(4):516−522. doi: 10.1002/iub.1991
[49]XU J, LI M, ZHANG Y, et al. Huangjinya black tea alleviates obesity and insulin resistance via modulating fecal metabolome in high-fat diet-fed mice[J]. Molecular Nutrition & Food Research,2020,64(22):e2000353.
[50] 张晓云, 梅晓宏. 板栗壳色素通过AMPK信号通路改善肥胖小鼠的脂代谢紊乱[J]. 中国食品学报,2023,23(7):177−186. [ZHANG Xiaoyun, MEI Xiaohong. Chestnut shells pigment ameliorated lipid metabolism disorder in obese mice through ampk signaling pathway[J]. Journal of Chinese Institute of Food Science and Technology,2023,23(7):177−186.]ZHANG Xiaoyun, MEI Xiaohong. Chestnut shells pigment ameliorated lipid metabolism disorder in obese mice through ampk signaling pathway[J]. Journal of Chinese Institute of Food Science and Technology, 2023, 23(7): 177−186.
[51]CHEN Y K, CHEUNG C, REUHL K R, et al. Effects of green tea polyphenol (-)-epigallocatechin-3-gallate on newly developed high-fat/Western-style diet-induced obesity and metabolic syndrome in mice[J]. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry,2011,59(21):11862−11871. doi: 10.1021/jf2029016
[52]ASHIGAI H, TANIGUCHI Y, SUZUKI M, et al. Fecal lipid excretion after consumption of a black tea polyphenol containing beverage–randomized, placebo-controlled, double-blind, crossover study[J]. Biological and Pharmaceutical Bulletin,2016,39(5):699−704. doi: 10.1248/bpb.b15-00662
[53] 杨丽聪, 郑国栋, 蒋艳, 等. 咖啡碱与茶多酚组合对小鼠肝脏脂肪代谢酶活性的影响[J]. 中国食品学报,2011,11(3):14−19. [YANG Licong, ZHENG Guodong, JIANG Yan, et al. Effects of caffeine and catechins combination on live lipids metabolism relative enzymes in mice[J]. Journal of Chinese Institute of Food Science and Technology,2011,11(3):14−19.]YANG Licong, ZHENG Guodong, JIANG Yan, et al. Effects of caffeine and catechins combination on live lipids metabolism relative enzymes in mice[J]. Journal of Chinese Institute of Food Science and Technology, 2011, 11(3): 14−19.
[54]BANERJEE S, GHOSHAL S, PORTER D T. Phosphorylation of hepatic AMP-activated protein kinase and liver kinase B1 is increased after a single oral dose of green tea extract to mice[J]. Nutrition Research,2012,32(12):985−990. doi: 10.1016/j.nutres.2012.10.005
相关知识
肥宅福音!绿茶+柑橘多酚=减肥降脂新搭档!
绿瘦茶多酚胶囊
陈莉明教授:抗肥胖药物研究进展、挑战及展望
研究进展
左旋肉碱茶多酚胶囊:助力健康减脂
我国的环境双酚A污染及其人体健康影响研究进展
肥胖潜在成因研究取得新进展
爱上多酚美食更健康
褐藻多糖改善肥胖及其并发症的研究进展
肥胖症康复治疗的研究进展.doc 文档全文免费预览
网址: 茶多酚抗肥胖的研究进展 https://m.trfsz.com/newsview376260.html

