一株引起番石榴黑斑病病原菌的分离与鉴定
摘要: 目的:旨在为明确番石榴黑斑病优势病原菌的种类及其特性提供科学依据。方法:从受黑斑病病害侵染的番石榴果实上分离纯化出一株优势病原菌,命名为S1,并对其进行形态学观察、致病性测定、生长特性研究及聚合酶链式反应(Polymerase Chain Reaction,PCR)测序比对分析,较为全面的对分离出的优势病原菌S1进行鉴定。结果:由形态学观察可知,S1菌落的气生菌丝蓬松且致密,颜色呈墨绿色或黑色,其孢子形态为单孢且透明,大小均匀,约为(6~10) μm×(6~7) μm,呈圆形或椭圆形,与《真菌鉴定手册》比对,初步判定其属叶点霉属菌,将其反接于健康番石榴果实上进行致病性测定。结果表明,S1为致使番石榴产生黑斑病的主导优势病原菌。通过生长特性研究表明,S1在偏碱性、黑暗、常温条件下较为适宜生长,结合PCR测序结果,确定出致使番石榴黑斑病的优势病原菌S1为首都叶点霉(Phyllosticta capitalensis)。结论:引起番石榴黑斑病的优势病原菌为首都叶点霉。
关键词: 番石榴 / 病原菌 / 鉴定 / 首都叶点霉Abstract: Objective: In order to provide scientific basis for further clarifying the species and characteristics of dominant pathogens causing guava black spot. Method: A dominant pathogen, named S1, was isolated and purified from the guava fruit infected with black spot disease, and subjected to morphology observation, pathogenicity determination, growth characteristics study and polymerase chain reaction (PCR) sequencing comparison analysis were conducted for comprehensive identification of the dominant pathogen S1. Results: According to the morphological observation, the aerial hyphae of the S1 colony were fluffy and dense, and the color was dark green or black. The spore morphology was monospore and transparent, and the size was uniform, about (6~10) μm×(6~7) μm, round or elliptical, compared with the "Fungus Identification Manual", it was preliminarily determined to belong to Phyllanthus spp., and once again inoculated to healthy guava fruits for pathogenicity determination. The results showed that S1 was the dominant pathogen causing guava black spot disease. Research on growth characteristics showed that S1 was more suitable for growth under alkaline, dark and normal temperature conditions. Moreover, S1 was identified as Phyllosticta capitalensis by the comparison of the PCR sequencing results. Conclusion: The dominant pathogen causing guava black spot disease was Phyllosticta capitalensis.
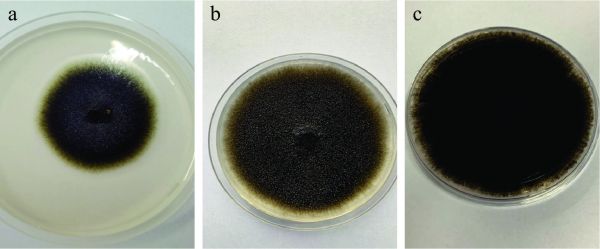
图 1 分离纯化菌落的形态
注:a:分离出的菌落;b:纯化后菌落(正面);c:纯化后菌落(背面)。
Figure 1. Morphology of isolated and purified colonies
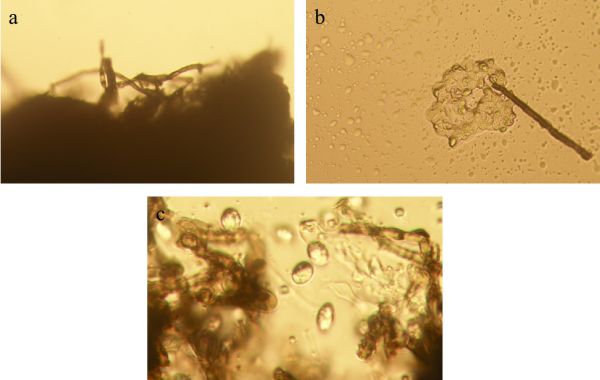
图 2 病原菌的显微形态
注:a:菌丝体(100×);b:分生孢子(200×);c:分生孢子(400×)。
Figure 2. Microscopic morphology of pathogens
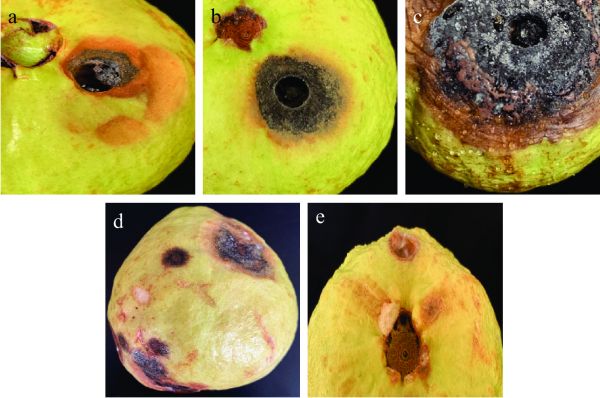
图 3 分离纯化菌株对番石榴的致病性
注:a:致病性测定结果(5 d);b:致病性测定结果(8 d);c:致病性测定结果(14 d);d:自然发病症状;e:致病性测定结果(空白组)。
Figure 3. Pathogenicity of isolated and purified strains to guava
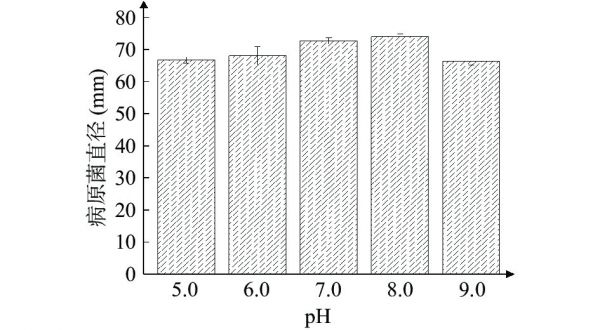
图 4 pH对病原菌菌丝的影响
Figure 4. Effect of pH on the hyphae of pathogenic bacteria
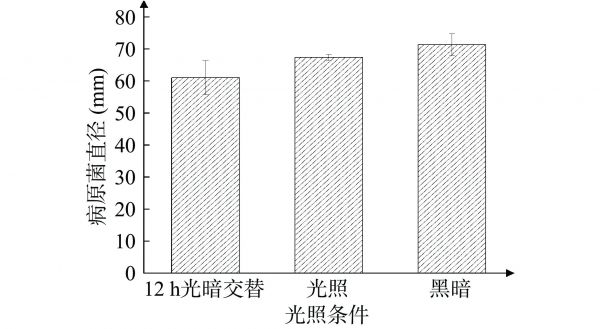
图 5 光照对病原菌菌丝的影响
Figure 5. Effect of light on the hyphae of pathogenic bacteria
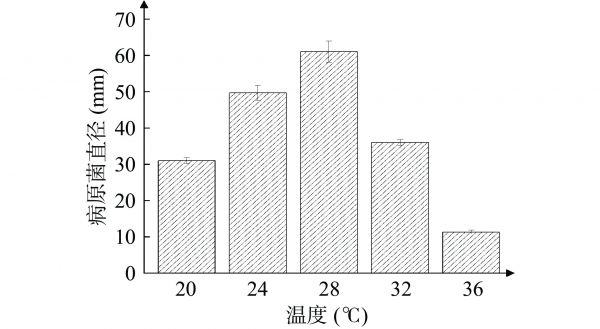
图 6 温度对病原菌菌丝的影响
Figure 6. Influence of temperature on the hyphae of pathogenic bacteria
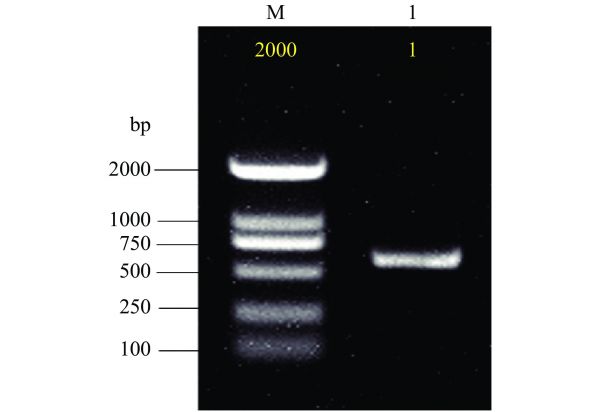
图 7 S1菌株PCR扩增产物的琼脂糖凝胶电泳图
注:M:标准DNA分子质量;1:菌株S1。
Figure 7. Agarose gel electrophoresis of PCR amplification products of strain S1
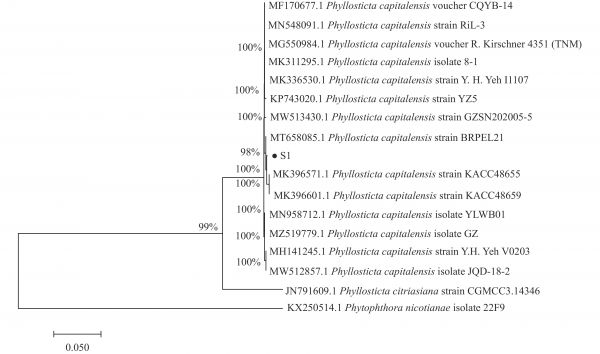
图 8 S1菌株基于rDNA-ITS序列构建的系统发育树
Figure 8. Phylogenetic tree constructed by S1 strain based on rDNA-ITS sequence
[1] 刘建林, 夏明忠, 袁颖. 番石榴的综合利用现状及发展前景[J]. 中国林副特产,2005,4(6):60−62. [LIU Jianlin, XIA Mingzhong, YUAN Ying. Psidium guajava integrated utlizaiton and its development prospects in China[J]. Forest By-product and Speciality in China,2005,4(6):60−62. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-6902.2005.06.036LIU Jianlin, XIA Mingzhong, YUAN Ying. Psidium guajava integrated utlizaiton and its development prospects in China[J]. Forest By-product and Speciality in China, 2005, 4(6): 60-62. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-6902.2005.06.036
[2] 彭燕, 张敏, 崔小丽, 等. 珍珠番石榴果实中的营养成分与活性物质分析[J]. 食品与机械,2020,36(8):36−40. [PENG Yan, ZHANG Min, CUI Xiaoli, et al. Analysis of nutrients and bioactive compounds in fruits of Psidium guajava l. cv. pearl[J]. Food & Machinery,2020,36(8):36−40.PENG Yan, ZHANG Min, CUI Xiaoli, et al. Analysis of nutrients and bioactive compounds in fruits of Psidium guajava l. cv. pearl[J]. Food & Machinery, 2020, 36(8): 36-40.
[3] 张朝坤, 黄婉莉, 陈洪彬, 等. 番石榴果实生长发育和营养品质变化规律分析[J]. 热带作物学报,2021,42(4):1035−1040. [ZHANG Chaokun, HUANG Wanli, CHEN Hongbin, et al. Analysis on the law of Psidium guajava L. fruit growth and nutritional quality[J]. Chinese Journal of Tropical Crops,2021,42(4):1035−1040. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-2561.2021.04.018ZHANG Chaokun, HUANG Wanli, CHEN Hongbin, et al. Analysis on the law of Psidium guajava L. fruit growth and nutritional quality[J]. Chinese Journal of Tropical Crops, 2021, 42(4): 1035-1040. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-2561.2021.04.018
[4] 孙锐, 孙蕾, 赵登超, 等. 不同石榴品种果实的营养成分比较分析[J]. 食品工业科技,2015,36(2):358−361. [SUN Rui, SUN Lei, ZHAO Dengchao, et al. Comparative analysis of nutritional ingredients in different kinds of pomegranate fruits[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry,2015,36(2):358−361.SUN Rui, SUN Lei, ZHAO Dengchao, et al. Comparative analysis of nutritional ingredients in different kinds of pomegranate fruits[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry, 2015, 36(2): 358-361.
[5]LI P Y, HSU C C, YIN M C, et al. Protective effects of red guava on inflammation and oxidative stress in streptozotocin-induced diabetic mice[J]. Molecules,2015,20(12):22341−22350. doi: 10.3390/molecules201219831
[6]HIRUDKAR J R, PARMAR K M, PRASAD R S, et al. The antidiarrhoeal evaluation of Psidium guajava L. against enteropathogenic Escherichia coli induced infectious diarrhoea[J]. Journal of Ethnopharmacology,2020,251:112561. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2020.112561
[7] 宋银雪, 高烨, 许静, 等. 番石榴叶总三萜对脓毒症大鼠急性肾损伤的治疗及对PI3K/AKT通路的调控[J]. 河北医药,2021,43(15):2270−2274. [SONG Yinxue, GAO Ye, XU Jing, et al. Therapeutic effects of total triterpenoids in guava leaves on acute kidney injury in septic rats and its regulation of PI3K/AKT pathway[J]. Hebei Medical Journal,2021,43(15):2270−2274. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-7386.2021.15.006SONG Yinxue, GAO Ye, XU Jing, et al. Therapeutic effects of total triterpenoids in guava leaves on acute kidney injury in septic rats and its regulation of PI3K/AKT pathway[J]. Hebei Medical Journal, 2021, 43(15): 2270-2274. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-7386.2021.15.006
[8]REZAEI M, LIU B. Food loss and waste in the food supply chain[J]. International Nut and Dried Fruit Council: Reus, Spain,2017:26−27.
[9]HWANG S G, LI Y Y, LIN H L. Excellent nutritional value in fruits of three guava cultivars in Taiwan[J]. Acta Horticulturae,2017,1166:209−213.
[10] 周浓, 杨锡洪, 解万翠, 等. “珍珠”番石榴的营养成分与挥发性风味特征分析[J]. 食品与机械,2016,32(2):37−40. [ZHOU Nong, YANG Xihong, XIE Wangcui, et al. Analysis of nutrition and valitile flavor of guava fruit (Psidium guajava L.)[J]. Food & Machinery,2016,32(2):37−40.ZHOU Nong, YANG Xihong, XIE Wangcui, et al. Analysis of nutrition and valitile flavor of guava fruit (Psidium guajava L. )[J]. Food & Machinery, 2016, 32(2): 37-40.
[11]PRUSKY D. Reduction of the incidence of postharvest quality losses, and future prospects[J]. Food Security,2011,3(4):463−474. doi: 10.1007/s12571-011-0147-y
[12] 张慧丽, 徐瑛, 段维军, 等. 番石榴黑斑病病原菌的分离鉴定[J]. 安徽农业科学,2011,39(28):17310−17311. [ZHANG Huili, XU Ying, DUAN Weijun, et al. Isolation and identification of black spot pathogen in Psidium guajava[J]. Journal of Anhui Agricultural Sciences,2011,39(28):17310−17311. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0517-6611.2011.28.073ZHANG Huili, XU Ying, DUAN Weijun, et al. Isolation and identification of black spot pathogen in Psidium guajava[J]. Journal of Anhui Agricultural Sciences, 2011, 39(28): 17310-17311. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0517-6611.2011.28.073
[13] 赵志常, 黄建峰. 番石榴炭疫病[J]. 世界热带农业信息,2019(8):43. [ZHAO Zhichang, HUANG Jianfeng. Guava anthracnose[J]. World Tropical Agriculture Information,2019(8):43.ZHAO Zhichang, HUANG Jianfeng. Guava Anthracnose[J]. World Tropical Agriculture Information, 2019, (8): 43.
[14]SOLARTE F, MUÑOZ C G, MAHARACHCHIKUMBURA S S N, et al. Diversity of Neopestalotiopsis and Pestalotiopsis spp., causal agents of guava scab in colombia[J]. Plant Disease,2018,102(1):49−59. doi: 10.1094/PDIS-01-17-0068-RE
[15] 高新明, 李本金, 兰成忠, 等. 番石榴焦腐病菌的ITS分析及PCR检测[J]. 植物保护学报,2011,38(3):227−232. [GAO Xinming, LI Benjin, LAN Chengzhong, et al. Analysis of ITS sequence and PCR detection of Botryosphaeria rhodina[J]. Journal of Plant Protection,2011,38(3):227−232.GAO Xinming, LI Benjin, LAN Chengzhong, et al. Analysis of ITS sequence and PCR detection of Botryosphaeria rhodina[J]. Journal of Plant Protection, 2011, 38(3): 227-232.
[16] 董汉松. 植病研究法[M]. 北京: 中国农业出版社, 2012DONG Hansong. Plant disease research method[M]. Beijing: China Agriculture Press, 2012.
[17]SANGER F, COULSON A R, BARRELL B G, et al. Cloning in single-stranded bacteriophage as an aid to rapid DNA sequencing[J]. Journal of Molecular Biology,1980,143(2):161−178. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(80)90196-5
[18]ARAFAT K. A novel isolate of Phyllosticta capitalensis causes black spot disease on guava fruit in Egypt[J]. Asian Journal of Plant Pathology,2018,12(1):27−37.
[19] SRISKULTEIW N. 番石榴黑星病之鉴定及感染源[D]. 台中: 中兴大学, 2014.SRISKULTEIW N. Identification and infection source of guava scab[D]. Taizhong: Zhongxing University, 2014.
[20] 魏景超. 真菌鉴定手册[M]. 上海: 上海科学技术出版社, 1979WEI Jingchao. Fungus identification manual[M]. Shanghai: Shanghai Science and Technology Press, 1979.
[21] 孙俊. 榛子叶斑病病原菌生物学特性[J]. 江苏农业科学,2017,45(7):101−103. [SUN Jun. Biological characteristics of the pathogen of hazelnut leaf spot[J]. Jiangsu Agricultural Sciences,2017,45(7):101−103.SUN Jun. Biological characteristics of the pathogen of hazelnut leaf spot[J]. Jiangsu Agricultural Sciences, 2017, 45(7): 101-103.
[22] 王晓梅, 黄琦, 李玉. 桂花叶斑病病原鉴定及其生物学特性研究[J]. 吉林农业大学学报,2011,33(2):151−157. [WANG Xiaomei, HUANG Qi, LI Yu. Pathogeny identification and biological characteristics of the leaf spot lesions of Osmamthus fragrans[J]. Journal of Jilin Agricultural University,2011,33(2):151−157.WANG Xiaomei, HUANG Qi, LI Yu. Pathogeny identification and biological characteristics of the leaf spot lesions of Osmamthus fragrans[J]. Journal of Jilin Agricultural University, 2011, 33(2): 151-157.
[23] 张桥. 桂花叶枯病病原菌生物学特性研究[J]. 现代农业科技,2016(11):153−154. [ZHANG Qiao. Study on the biological characteristics of the pathogen of Osmanthus fragrans leaf blight[J]. Modern Agricultural Science and Technology,2016(11):153−154. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-5739.2016.11.097ZHANG Qiao. Study on the biological characteristics of the pathogen of Osmanthus fragrans leaf blight[J]. Modern Agricultural Science and Technology, 2016(11): 153-154. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-5739.2016.11.097
[24] 王正贤, 朱文倩, 黄奕蔓, 等. 广西玉林市番石榴焦腐病的病原菌鉴定[J]. 植物病理学报,2021,51(5):813−816. [WANG Zhengxian, ZHU Wenqian, HUANG Yiman, et al. Identification of the pathogen causing guava black-rot in Yulin, Guangxi[J]. Acta Phytopathologica Sinica,2021,51(5):813−816.WANG Zhengxian, ZHU Wenqian, HUANG Yiman, et al. Identification of the pathogen causing guava black-rot in Yulin, Guangxi[J]. Acta Phytopathologica Sinica, 2021, 51(5): 813-816.
[25] 刘任, 戚佩坤. 广州地区番石榴病害鉴定[J]. 仲恺农业技术学院学报,1991,4(1):38−46. [LIU Ren, QI Peikun. Identification on the diseases of guava in Guangzhou District[J]. Journal of Zhongkai Agrotechnical College,1991,4(1):38−46.LIU Ren, QI Peikun. Identification on the diseases of guava in Guangzhou District[J]. Journal of Zhongkai Agrotechnical College, 1991, 4(1): 38-46.
[26]LAN C, YAO J, YANG X, et al. Specific and sensitive detection of the guava fruit anthracnose pathogen (Colletotrichum gloeosporioides) by loop-mediated isothermal amplification (LAMP) assay[J]. Microbiology,2020,66(1):17−24.
[27] 张志华, 洪葵. 核酸序列直接分析在真菌鉴定方面的应用[J]. 华南热带农业大学学报,2006,12(2):39−43. [ZHANG Zhihua, HONG Kui. Application of nucleic ACID sequence analysis in fungi taxonmy[J]. Journal of South China University of Tropical Agrjculture,2006,12(2):39−43.ZHANG Zhihua, HONG Kui. Application of nucleic ACID sequence analysis in fungi taxonmy[J]. Journal of South China University of Tropical Agrjculture, 2006, 12(2): 39-43.
[28]SAOWANEE W, LORENZO L, PEDRO W, et al. Phylosticta capialensis, a widespread endophyte of plants[J]. Fungal Diversity,2013,60(1):91−105. doi: 10.1007/s13225-013-0235-8
[29] 赵杏利, 胡镇杰, 侯典云, 等. 牡丹内生真菌MD76的鉴定及次级代谢产物研究[J]. 中国药学杂志,2018,53(21):1826−1830. [ZHAO Xingli, HU Zhenjie, HOU Dianyun, et al. Identification and secondary metabolites of endophytic fungus MD76 from Paeonia suffruticosa[J]. Chinese Pharmaceutical Journal,2018,53(21):1826−1830.ZHAO Xingli, HU Zhenjie, HOU Dianyun, et al. Identification and secondary metabolites of endophytic fungus MD76 from Paeonia suffruticosa[J]. Chinese Pharmaceutical Journal, 2018, 53(21): 1826-1830.
[30] 张建芬, 林璟, 徐好仪, 等. 华泽兰内生真菌的分离及其抑菌、抗肿瘤活性[J]. 中成药,2020,42(1):133−138. [ZHANG Jianfen, LIN Jing, XU Haoyi, et al. Isolation of endophytic fungi from eupatorium Chinense and their antimicrobial, antitumor activities[J]. Chinese Traditional Patent Medicine,2020,42(1):133−138. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-1528.2020.01.029ZHANG Jianfen, LIN Jing, XU Haoyi, et al. Isolation of endophytic fungi from eupatorium Chinense and their antimicrobial, antitumor activities[J]. Chinese Traditional Patent Medicine, 2020, 42(1): 133-138. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-1528.2020.01.029
[31]DUAN C H, CHANG C M, SU C C, et al. Phyllosticta capitalensis causes black spot on persimmon (Diospyros kaki) fruit in Taiwan[J]. Australasian Plant Disease Notes,2017,12(1):1−4. doi: 10.1007/s13314-016-0226-1
[32]PURBAJANTI E D, SETIADI A, ROESSALI W. Variability and nutritive compounds of guava (Psidium guajava L.)[J]. Indian Journal of Agricultural Research,2016,50(3):273−277.
[33]SOARES-COLLETTI A R, FISCHER I H, LOURENÇO S D A. The effects of temperature and wetness duration on the development of Guignardia psidii in guava fruit naturally infected[J]. Australasian Plant Pathology,2015,44(4):413−418. doi: 10.1007/s13313-014-0327-2
[34] 肖倩莼, 陈永强, 余卓桐, 等. 主要热带果树煤烟病的为害性及病原菌种类研究[J]. 热带作物学报,2000,21(1):25−30. [XIAO Qianchun, CHEN Yongqiang, YU Zhuodong, et al. A study on sooty moulds of tropical fruit crops and their pathogens[J]. Chinese Journal of Tropical Crops,2000,21(1):25−30. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-2561.2000.01.005XIAO Qianchun, CHEN Yongqiang, YU Zhuodong, et al. A Study on sooty moulds of tropical fruit crops and their pathogens[J]. Chinese Journal of Tropical Crops, 2000, 21(1): 25-30. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-2561.2000.01.005
相关知识
番石榴的15个功效与作用
【番石榴叶】番石榴叶的功效与作用
番石榴茶
番石榴叶茶:健康与美丽的双重守护
番石榴叶的营养价值和功效
番石榴叶泡水喝的功效
番石榴叶子的功效
番石榴叶的功效与作用禁忌
番石榴叶泡水喝的功效与作用
芭乐是番石榴吗?芭乐与番石榴的区别,你还傻傻的分不清吗?
网址: 一株引起番石榴黑斑病病原菌的分离与鉴定 https://m.trfsz.com/newsview459642.html