基于电化学模型的锂离子电池健康状态估算
摘要: 针对电动汽车锂离子电池健康状态在线估算问题,提出了一种基于伪二维模型参数的估算方法. 该方法通过拆解同类估算目标电池,以扫描电镜测量电池结构参数,利用遗传算法辨识其他未知电化学模型参数,建立一种新的基于化学计量比的电池正极容量计算法则,估算电池健康状态. 同时考虑老化对电池正极化学计量比的影响,进一步提高健康状态估算精度. 采用电池老化数据集验证该方法的有效性,结果表明所提出的估算方法能在短时动态工况下实现电池健康状态的准确在线估算.
Abstract: To estimate online health state of Li-Ion batteries in electric vehicles accurately, a method was proposed based on the parameters of a pseudo-two-dimensional model. Firstly, disassembling congeneric objective batteries and measuring their structural parameters using scanning electron microscopy, the method was arranged to get some unknown parameters based on genetic algorithm for an electrochemical model. Then, a new stoichiometry ratio-based battery positive capacity calculation was established to estimate the health state of battery. Considering the influence of aging on the stoichiometry ratio in the positive electrode, the estimation accuracy of health state was further improved. Finally, a battery aging dataset was used to verify the validity of the method. The results show that the proposed estimation method can achieve an accurate online estimation of battery health state in short dynamic loading.
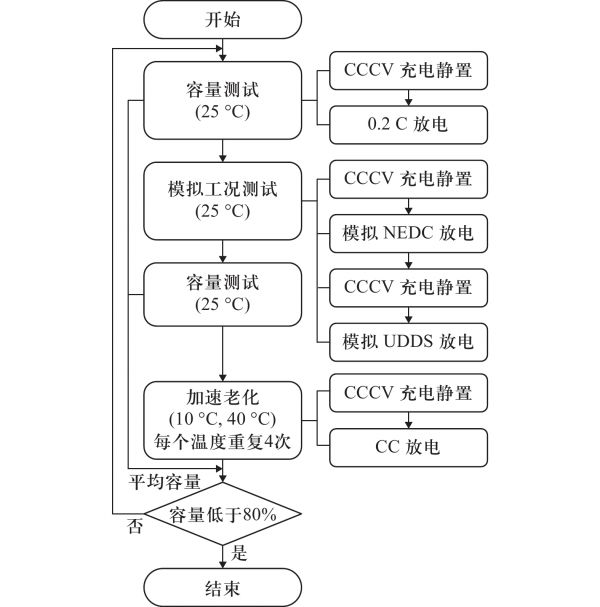
图 1 老化实验流程
Figure 1. The flowchart of aging experiment
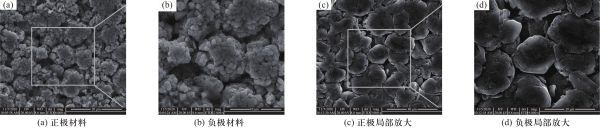
图 2 电极材料及局部放大
Figure 2. Electrode material and partial zoom
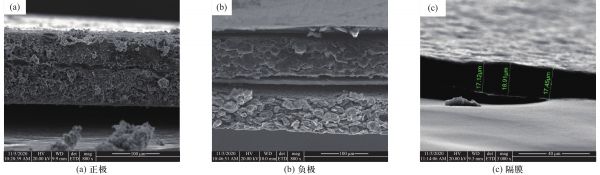
图 3 电池结构厚度测量
Figure 3. Thickness measurement
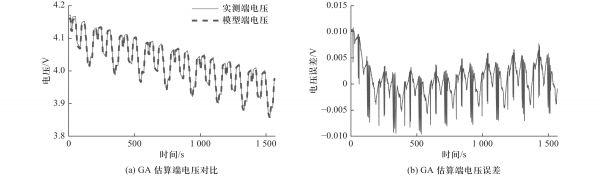
图 4 P2D模型评估
Figure 4. Evaluation of P2D model
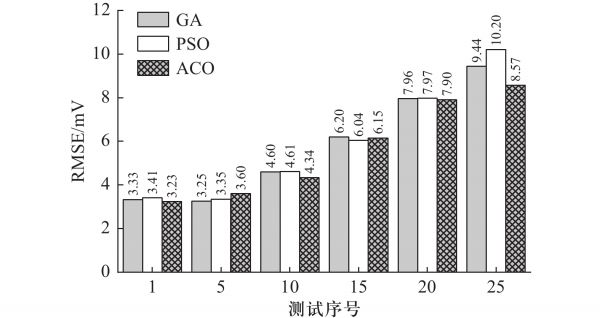
图 5 不同优化方法的辨识精度
Figure 5. Identification accuracy of different optimization methods
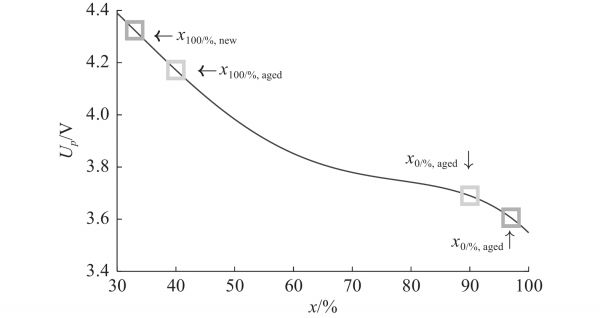
图 6 老化过程中的正极化学计量比的变化
Figure 6. The stoichiometric proportion of aging process
表 1 SOH估算误差
Table 1 Errors of SOH estimation
容量测试序号电池真实容量/Ah修正前误差/%修正后误差/%SAM1SAM2SAM1SAM2SAM1SAM2 12.6282.7100.000.000.000.0052.5972.6721.161.461.111.46102.5822.6560.141.59−0.170.61152.4642.600 5.052.892.520.39202.2442.5063.642.841.66−0.17251.9292.4064.402.880.720.54301.9812.941.91MAE2.402.091.030.73RMSE3.152.331.350.97表 2 SOH估算误差对比
Table 2 Comparison of errors of SOH estimation
方法索引及方法平均绝对误差/%平均绝对误差的均值/% 模型法文献[4], 电化学模型1.61, 2.522.07文献[5], 等效电路模型11数据
驱动法文献[6], 优化拟合模型约1.02, 0.98, 0.59, 0.97,
1.03, 0.82 0.97 ,
0.67 ,1.060.90文献[8], 神经网络3.52, 3.41, 3.25, 2.793.24文献[9], 极限学习机1.121.12文献[10], 高斯过程回归3.70, 1.00, 0.521.74文中方法1.03, 0.730.88 [1] 陈德海, 华铭, 邹争明, 等. 优化分级T-S模糊控制动态估计纯电动汽车电池健康状态[J]. 北京理工大学学报, 2019, 39(6):609 − 614.
CHEN Dehai, HUA Ming, ZOU Zhengming, et al. Dynamic prediction of pure electric vehicle battery state of health by optimized and graded t-s fuzzy control[J]. Transactions of Beijing Institute of Technology, 2019, 39(6):609 − 614. (in Chinese)
[2] 庞晓琼, 王竹晴, 曾建潮, 等. 基于PCA-NARX的锂离子电池剩余使用寿命预测[J]. 北京理工大学学报, 2019, 39(4):406 − 412.PANG Xiaoqiong, WANG Zhuqing, ZENG Jianchao, et al. Prediction for the remaining useful life of lithium-ion battery based on PCA-NARX[J]. Transactions of Beijing Institute of Technology, 2019, 39(4):406 − 412. (in Chinese)
[3]LI J, ADEWUYI K, LOTFI N, et al. A single particle model with chemical/mechanical degradation physics for lithium ion battery State of Health (SOH) estimation[J]. Applied Energy, 2018, 212:1178 − 1190. doi: 10.1016/j.apenergy.2018.01.011
[4]XIONG Rui, LI Linlin, LI Zhirun, et al. An electrochemical model based degradation state identification method of Lithium-ion battery for all-climate electric vehicles application[J]. Applied Energy, 2018, 219:264 − 275. doi: 10.1016/j.apenergy.2018.03.053
[5] 陈猛, 乌江, 焦朝勇, 等. 锂离子电池健康状态多因子在线估计方法[J]. 西安交通大学学报, 2020, 54(1):169 − 175.CHEN Meng, WU Jiang, JIAO Chaoyong, et al. Multi-factor online estimation method for health status of lithium-ion battery[J]. Journal of Xi'an Jiaotong University, 2020, 54(1):169 − 175. (in Chinese)
[6] 南金瑞, 孙路. 基于粒子群算法估计实际工况下锂电池SOH[J]. 北京理工大学学报, 2021, 41(1):59 − 64.NAN Jinrui, SUN Lu. Estimation of lithium battery soh under actual operating conditions based on particle swarm optimization[J]. Transactions of Beijing Institute of Technology, 2021, 41(1):59 − 64. (in Chinese)
[7]YANG Duo, ZHANG Xu, PAN Rui, et al. A novel Gaussian process regression model for state-of-health estimation of lithium-ion battery using charging curve[J]. Journal of Power Sources, 2018, 384:387 − 395. doi: 10.1016/j.jpowsour.2018.03.015
[8]ZHANG Shuzhi, ZHAI Baoyu, GUO Xu, et al. Synchronous estimation of state of health and remaining useful lifetime for lithium-ion battery using the incremental capacity and artificial neural networks[J]. Journal of Energy Storage, 2019, 26:100951. doi: 10.1016/j.est.2019.100951
[9]CHEN Lin, WANG Huimin, LIU Bohao, et al. Battery state-of-health estimation based on a metabolic extreme learning machine combining degradation state model and error compensation[J]. Energy, 2021, 215:119078. doi: 10.1016/j.energy.2020.119078
[10]ROMAN Darius, SAXENA Saurabh, ROBU Valentin, et al. Machine learning pipeline for battery state-of-health estimation[J]. Nature Machine Intelligence, 2021, 3(5):447 − 456. doi: 10.1038/s42256-021-00312-3
[11]KHODADADI Sadabadi Kaveh, JIN Xin, RIZZONI Giorgio. Prediction of remaining useful life for a composite electrode lithium ion battery cell using an electrochemical model to estimate the state of health[J]. Journal of Power Sources, 2021, 481:228861. doi: 10.1016/j.jpowsour.2020.228861
[12]LÜ Zhiqiang, GAO Renjing. A model‐based and data‐driven joint method for state‐of‐health estimation of lithium‐ion battery in electric vehicles[J]. International Journal of Energy Research, 2019, 43:7956 − 7969.
[13]XIONG Rui. Battery management algorithm for electric vehicles[M]. Singapore: Springer, 2020.
相关知识
《电动自行车用锂离子电池健康评估工作指引》解读
工信部:拟建立科学、准确、简便的锂离子电池健康评估流程和判定规则
工信部拟进一步加强电动自行车用锂离子电池健康评估工作
科学制定健康评估工作指引消除电动自行车用锂离子电池安全隐患
科学制定健康评估工作指引 消除电动自行车用锂离子电池安全隐患
工信部将公布电动自行车用锂电池健康评估网点
如何判断电动自行车用锂电池是否健康?工信部发布最新文件
医疗设备锂电池解决方案【钜大锂电】
健康状态评估
电池健康检测首进社区 为居民电动自行车深度“体检”
网址: 基于电化学模型的锂离子电池健康状态估算 https://m.trfsz.com/newsview561911.html