同行致远
关注
编者按:肥胖已成为全球亟需应对的公共健康问题。《2025年世界肥胖报告》指出,到2030年,全球将有超过29亿成年人的体重超重(BMI≥25 kg/m²),其中11亿人将达到肥胖标准(BMI≥30 kg/m²)。肥胖与2型糖尿病、高血压、冠心病、中风及多种癌症等慢性疾病密切相关,因此探索安全有效的减重手段已刻不容缓。可喜的是,司美格鲁肽和替尔泊肽等创新多肽药物的上市为肥胖治疗带来了重大突破。新一代减重疗法通过靶向多条关键信号通路,不但有望实现更显著的减重效果,还可能帮助维持肌肉质量、降低停药后的体重反弹,为肥胖患者提供更高质量的减重方案。为推动这类疗法的研发,药明康德旗下WuXi Biology已建立了多种模拟人体肥胖的动物模型,帮助合作伙伴在临床前阶段高效、精准地评估候选药物。本文将介绍新一代减重疗法的开发方向,以及药明康德的一体化CRDMO平台在这一领域的赋能能力。
靶向多重信号通路,提高减重效果
靶向多重信号通路是多款目前处于后期临床阶段的减重疗法的重要研发趋势。这些疗法靶向的信号通路包括胰高血糖素样肽-1(GLP-1),葡萄糖依赖性促胰岛素多肽(GIP)、胰高血糖素(GCG)、胰淀素等肠促胰岛素。例如,安进公司的MariTide、诺和诺德的CagriSema、以及礼来公司的retatrutide,通过同时作用于多条关键信号通路,有望更有效地调节食欲、能量摄入和能量消耗,从而实现更显著的减重效果。
不过,临床前研究面临的关键挑战之一,是标准啮齿类动物模型能否准确反映多靶点药物的综合疗效。例如,GLP-1受体激动剂司美格鲁肽在人体和高脂饮食诱导肥胖(DIO)小鼠模型中均表现出显著减重效果,原因在于两者GLP-1受体的高度同源性。相比之下,激活GIP和GLP-1受体的双靶点药物替尔泊肽情况则更为复杂:在人类中,其疗效依赖于两种受体的协同作用,但在常规DIO小鼠中,阻断GLP-1受体会完全消除替尔泊肽的疗效,而阻断GIP受体则对胰岛素分泌或血糖调节作用影响不大。这种差异表明,该药在小鼠中的效果主要来自GLP-1受体激活。这种差异很可能源于人和小鼠GIP受体的氨基酸序列同源性较低,使得小鼠模型无法完全复制人体药理反应。
为解决这一问题,WuXi Biology的代谢疾病团队开发了表达人类GIP受体的DIO小鼠模型。实验结果显示,与常规DIO小鼠相比,该模型在评估同时靶向GLP-1受体和GIP受体的减重药物时,能更好地体现双靶点药物的协同减重效果,并更准确反映药物对白色与棕色脂肪组织的作用。这些结果表明,表达人类GIP受体的小鼠模型能够更准确地反映人体药理反应,为评估多靶点减重药物的疗效提供更具转化价值的数据信息。
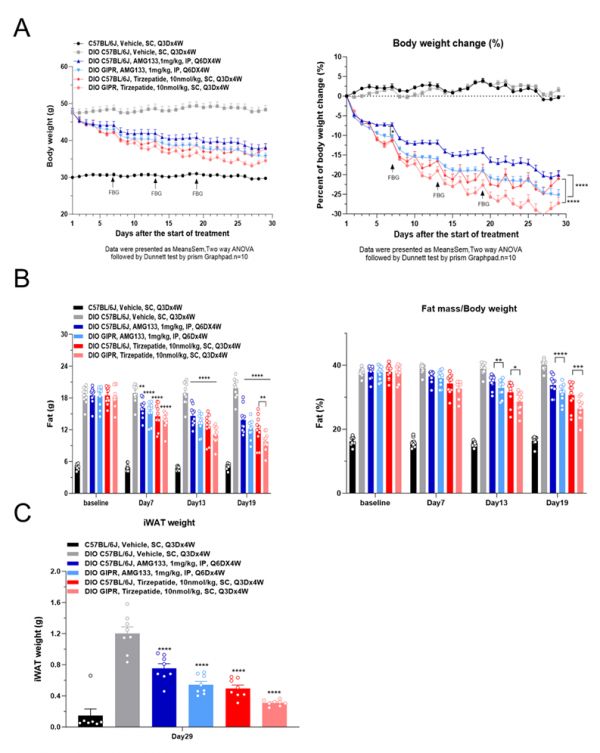
▲表达人类GIP受体的DIO小鼠模型评估多种减肥药物的实验结果(图片来源:参考资料[1])
减脂不减肌,长期健康减重的下一步
虽然GLP-1类药物能显著降低体重,但研究发现,减掉的体重中部分来自肌肉流失,这可能导致肌力下降、活动能力减弱及整体健康受损,在老年人中尤为值得关注。因此,保持肌肉质量是实现长期健康减重的重要方向之一。
目前,靶向雄激素受体、激活素受体以及肌肉生长抑制素等信号通路的多种候选药物已进入临床开发阶段,与GLP-1类药物联合使用时,可在减少脂肪的同时维持甚至增加瘦体重。WuXi Biology的研究团队也在实验中验证其开发的小鼠肥胖模型,能够在临床前研究中准确反映创新药物保存肌肉质量的效果。同时,团队具备进行多种肌肉功能检测的能力,包括对啮齿类动物肌肉力量和耐力的检测。
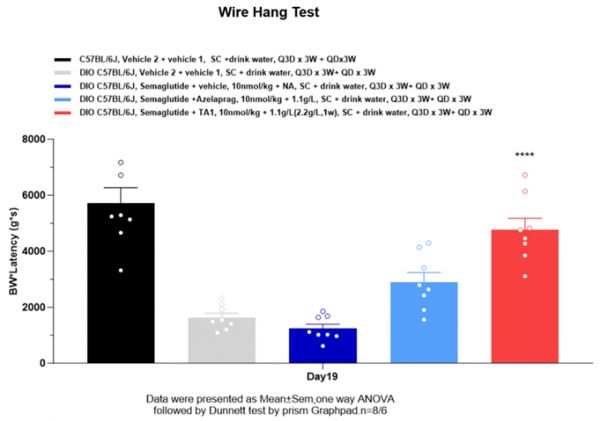
▲在小鼠模型中开展的肌肉功能检测结果(图片来源:参考资料[1])
传统行为学测试容易受到个体差异和操作者因素影响,导致数据一致性不足。此外,由于肥胖个体活动水平普遍下降,评估抗肥胖药物对肌肉功能的影响也面临挑战。为克服这些限制,WuXi Biology开发了更精细、客观的电生理检测平台,通过监测肌纤维特征变化并量化肌肉应力,更全面、准确地评估肌肉功能与药效。
防止体重反弹,延长疗效持久性
减重药物研发的另一大目标,是确保疗效的持久性。部分药物在停用后会引起体重快速反弹,不仅削弱疗效,还可能带来额外健康风险。因此,需要能够模拟停药后体重回升过程的临床前模型。
WuXi Biology团队已在DIO小鼠模型中开展了体重回升研究:在既定治疗期结束后停药,并持续观察3-4周。结果显示,停药后药物的抑制食欲作用迅速减弱,一些动物的进食量甚至超过对照组,导致体重明显回升。值得注意的是,回升的体重主要来自脂肪质量,而在减重阶段减少的则包括肌肉和脂肪。这种以脂肪为主的反弹不仅降低了治疗净收益,还可能恶化代谢状况。
▲在DIO小鼠模型中开展的体重回升研究结果(图片来源:参考资料[1])
这些发现强调了研发能够实现持久减重并在停药后最大限度减少反弹的药物的重要性。目前,靶向黑皮质素4受体(MC4R)、酰基辅酶A合成酶5(ACSL5)、以及激活素受体等信号通路的创新药物已经表现出减少GLP-1药物停用后体重反弹的效果。
今年,《自然》杂志上发表的一篇评论文章指出,减重疗法领域正迎来一个飞速发展的时期,创新疗法不断涌现。在药明康德,我们提供一体化研发服务,加速肥胖及相关代谢性疾病创新疗法的开发。药明康德的CRDMO平台可支持合作伙伴从早期发现到临床开发的全流程,涵盖药物化学、生物学以及临床前测试等多个领域的专业能力。展望未来,药明康德将持续赋能合作伙伴的减重药物开发,早日将科学创新转化为造福患者的新药好药。
The Next-Generation Weight Loss Therapies Are Coming
Obesity has become a pressing public health challenge worldwide. According to the 2025 World Obesity Atlas, by 2030, more than 2.9 billion adults globally will be overweight (BMI ≥ 25 kg/m²), of which 1.1 billion will meet the criteria for obesity (BMI ≥ 30 kg/m²). Obesity is closely linked to chronic diseases such as type 2 diabetes, hypertension, coronary heart disease, stroke, and various cancers, which makes the development of safe, effective weight-loss interventions an urgent priority.
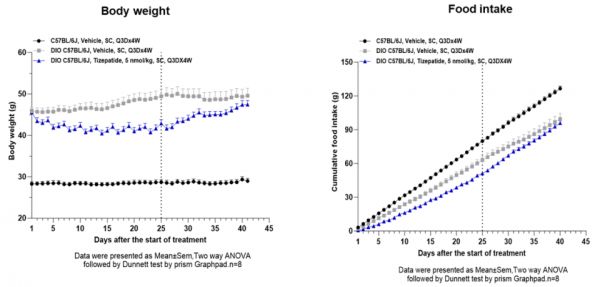
In recent years, the launch of innovative peptide drugs such as semaglutide and tirzepatide has marked a major breakthrough in obesity treatment. The next generation of weight-loss therapies aims to go further—targeting multiple key signaling pathways to deliver greater weight reduction, while also preserving muscle mass and reducing post-treatment weight regain. These approaches promise higher-quality, longer-lasting solutions for patients with obesity. To advance such therapies, WuXi Biology, a key part of WuXi AppTec, has developed a range of animal models that closely simulate human obesity, enabling partners to evaluate drug candidates efficiently and with high translational relevance at the preclinical stage.
Targeting Multiple Pathways to Boost Weight-Loss Efficacy
One prominent trend in late-stage clinical development is the design of therapies that act on multiple signaling pathways, including glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1), glucose-dependent insulinotropic polypeptide (GIP), glucagon (GCG), and amylin. By acting on more than one pathway to regulate appetite, energy intake, and expenditure more effectively, they can potentially achieve more pronounced weight loss.
However, preclinical evaluation of such drugs presents unique challenges. While GLP-1 receptor agonists like semaglutide demonstrate strong, consistent weight-loss effects in both humans and high-fat diet-induced obese (DIO) mouse models—thanks to high GLP-1 receptor homology between species—the picture is more complex for dual-target agents like tirzepatide. In humans, tirzepatide’s efficacy depends on the combined activation of GIP and GLP-1 receptors. Yet, in conventional DIO mice, blocking GLP-1 receptors eliminates efficacy, while blocking GIP receptors has minimal impact. This discrepancy stems from the lower amino acid sequence homology of GIP receptors between mice and humans, limiting the mouse model’s ability to replicate human pharmacological responses.
To address this gap, WuXi Biology’s metabolic disease team developed a DIO mouse model expressing the human GIP receptor. Studies showed that, compared to conventional DIO mice, this model more accurately reproduced the synergistic weight-loss effects of dual GLP-1/GIP receptor activation, as well as effects on white and brown adipose tissues. These results provide a more reliable foundation for evaluating multi-target obesity therapies in preclinical research.
Fat Loss Without Muscle Loss: Supporting Long-Term Health
While GLP-1 drugs can significantly reduce body weight, research shows that part of this loss comes from lean body mass. In older adults especially, muscle loss can reduce strength, mobility, and overall health. Preserving muscle mass has therefore become a key goal in next-generation weight-loss drug development.
Several candidates now in clinical development target pathways such as the androgen receptor, activin receptor, and myostatin signaling. In combination with GLP-1 drugs, they aim to reduce fat while maintaining or even increasing lean body mass. WuXi Biology has validated the ability of its obesity models to capture these effects in preclinical studies, with capabilities for detailed muscle function testing, including strength and endurance assays in rodents.
Traditional behavioral muscle function tests, however, can be influenced by individual variability and operator technique, leading to inconsistent results—particularly in obese subjects with naturally lower activity levels. To overcome these limitations, WuXi Biology employed a more refined and objective approach using electrophysiological platforms to monitor changes in muscle fiber characteristics and quantify muscle stress. This method provides a more comprehensive and accurate assessment of muscle function and drug efficacy.
Preventing Weight Regain: Extending the Benefits of Therapy
Another major challenge is sustaining weight loss over time. Many drugs lead to rapid weight regain after discontinuation, negating the benefits and potentially worsening health risks. This makes preclinical models that simulate post-treatment weight regain essential for drug development.
In DIO mouse models, WuXi Biology researchers studied the post-discontinuation period by observing animals for 3–4 weeks after treatment stopped. Appetite-suppressing effects diminished quickly, with some animals eating even more than controls. Most of the regained weight came from fat, while weight lost during treatment had included both fat and muscle. This fat-dominant rebound reduces overall health benefits and may further impair metabolic function.
Encouragingly, emerging drug candidates targeting melanocortin-4 receptor (MC4R), acyl-CoA synthetase long-chain family member 5 (ACSL5), and activin receptors have shown the ability to limit weight regain after stopping GLP-1 therapy.
A recent Nature commentary highlighted that weight-loss therapy is entering a period of rapid expansion, with a growing pipeline of innovative treatments. At WuXi AppTec, we offer integrated R&D services to accelerate the development of innovative therapies for obesity and related metabolic disorders. Our platform supports partners from early discovery through clinical development, providing expertise in areas such as medicinal chemistry, biology, and preclinical testing. Looking ahead, WuXi AppTec will continue to leverage its fully integrated, end-to-end CRDMO platform to support partners in advancing novel weight-loss drugs, ultimately helping to transform scientific breakthroughs into life-changing therapies for patients worldwide.
参考资料:
[1] Innovative R&D Strategies for Peptide Drugs in Obesity Treatment. Retrieved August 11, 2025, from https://wuxibiology.com/resource/innovative-rd-strategies-for-peptide-drugs-in-obesity-treatment/
[2] 2025年世界肥胖报告. Retrieved August 13, 2025, from https://data.worldobesity.org/publications/atlas-2025-cn.pdf
[3] 32nd European Congress on Obesity. Retrieved August 13, 2025, from https://wuxibiology.com/32nd-european-congress-on-obesity/
免责声明:本文仅作信息交流之目的,文中观点不代表药明康德立场,亦不代表药明康德支持或反对文中观点。本文也不是治疗方案推荐。如需获得治疗方案指导,请前往正规医院就诊。免责声明:本内容来自腾讯平台创作者,不代表腾讯新闻或腾讯网的观点和立场。
 举报
举报
相关知识
行稳致远 重在协同
送教交流促均衡,笃行致远共成长
猫科团队主任兽医马云峰:知行合一,笃行致远
笃行致远 砥砺前行Volunteer service Forge ahead .
【地评线】太阳鸟时评:促进直播带货规范 推动行业行稳致远
“行而不辍 履践致远”大学生原创心理健康公益广告大赛结果揭晓
[健康之路]与奥运同行 一起动起来 3 学会骑行技巧 远离运动疼痛
在“热辣”中努力坚持 在“滚烫”中实现梦想—行远育才开学致辞
青岛市税务局税惠添翼 护航电商新业态行稳致远
咖啡致癌?远不如炸鸡“危险”
网址: 同行致远 https://m.trfsz.com/newsview1810372.html