The impact of comprehensive healthy lifestyles on obstructive sleep apnea and the mediating role of BMI: insights from NHANES 2005
The impact of comprehensive healthy lifestyles on obstructive sleep apnea and the mediating role of BMI: insights from NHANES 2005-2008 and 2015-2018
Jinsong Mou et al. BMC Pulm Med. 2024.
Abstract
Objective: In this study, the associations between healthy lifestyles and obstructive sleep apnea (OSA) in middle-aged and elderly adults were investigated via data from the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (NHANES) for the periods of 2005-2008 and 2015-2018.
Methods: A total of 6,406 participants aged 40 years and older were included in the analysis. Healthy lifestyle behaviors were assessed through diet quality, physical activity, sleep duration, alcohol consumption, smoking status, and body mass index (BMI). A composite healthy lifestyle score (ranging from 0 to 6) was created and categorized into insufficient (0-2), intermediate (3-4), and optimal (5-6) health groups. Weighted logistic regression models were used to examine the association between these lifestyle scores and OSA, adjusting for some demographic, socioeconomic, and clinical covariates. Additionally, mediation analysis was conducted to evaluate the role of BMI as a mediator in the relationship between the composite healthy lifestyle score and OSA, determining the proportion of the total effect mediated by BMI.
Results: Participants were classified into insufficient (17.81%), intermediate (56.82%), and optimal (25.37%) lifestyle groups. Higher dietary quality (OR: 0.81, 95% CI: 0.66-0.99) and adequate weight (OR: 0.09, 95% CI: 0.07-0.11) were statistically associated with reduced OSA odds after adjustments, whereas the variables were not. Each one-point increase in the healthy lifestyle score was linked to a 33% reduction in OSA odds (OR: 0.67, 95% CI: 0.63-0.71). A significant linear trend was observed, with better adherence to healthy lifestyle correlating with lower odds of OSA (p for trend < 0.001). Compared with insufficient lifestyle, intermediate lifestyle was linked to a 27% reduction in OSA (OR: 0.73, 95% CI: 0.58-0.91), whereas optimal lifestyle was associated with a 74% reduction (OR: 0.26, 95% CI: 0.21-0.33). Mediation analysis revealed that BMI significantly mediated the relationship between healthy lifestyle score and OSA, accounting for approximately 59.2% of the total effect (P < 0.001). The direct effect of the healthy lifestyle score on OSA remained significant even when controlling for BMI (P < 0.001). Subgroup analyses confirmed consistent benefits across different demographic groups.
Conclusions: This study revealed that adherence to healthy lifestyles significantly reduces the odds of OSA, with optimal lifestyles leading to a marked decrease in the odds of OSA. Notably, BMI plays a critical mediating role in this relationship. These findings emphasize the importance of promoting healthy lifestyle interventions as a key strategy for the prevention and management of OSA.
Keywords: Body Mass Index; Elderly Population; Healthy lifestyle; Mediation analysis; Obstructive sleep apnea; Public Health.
© 2024. The Author(s).
PubMed Disclaimer
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Ethics approval and consent to participate: The NHANES program was approved by the National Center for Health Statistics Ethics Review Board, and all participants provided written informed consent. Consent for publication: Not applicable. Clinical trial number: Not applicable. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
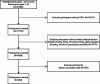 Fig. 1
Fig. 1 Flow chart of the study participants selection
 Fig. 2
Fig. 2 Linear relationship between healthy lifestyle score and OSA
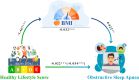 Fig. 3
Fig. 3 Mediating Effect of BMI on the relationship between healthy lifestyle and OSA
 Fig. 4
Fig. 4 Association between healthy lifestyle score and OSA, stratified by subgroup
Similar articles
Association between adherence to life's simple 7 metrics and risk of obstructive sleep apnea among adults in the United States.
Wu S, Yang YM, Zhu J, Wang LL, Xu W, Lyu SQ, Wang J, Shao XH, Zhang H. Wu S, et al. BMC Psychiatry. 2024 Aug 13;24(1):560. doi: 10.1186/s12888-024-05990-y. BMC Psychiatry. 2024. PMID: 39138439 Free PMC article.
Falls prevention interventions for community-dwelling older adults: systematic review and meta-analysis of benefits, harms, and patient values and preferences.
Pillay J, Gaudet LA, Saba S, Vandermeer B, Ashiq AR, Wingert A, Hartling L. Pillay J, et al. Syst Rev. 2024 Nov 26;13(1):289. doi: 10.1186/s13643-024-02681-3. Syst Rev. 2024. PMID: 39593159 Free PMC article.
Comparison of Two Modern Survival Prediction Tools, SORG-MLA and METSSS, in Patients With Symptomatic Long-bone Metastases Who Underwent Local Treatment With Surgery Followed by Radiotherapy and With Radiotherapy Alone.
Lee CC, Chen CW, Yen HK, Lin YP, Lai CY, Wang JL, Groot OQ, Janssen SJ, Schwab JH, Hsu FM, Lin WH. Lee CC, et al. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2024 Dec 1;482(12):2193-2208. doi: 10.1097/CORR.0000000000003185. Epub 2024 Jul 23. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2024. PMID: 39051924
Depressing time: Waiting, melancholia, and the psychoanalytic practice of care.
Salisbury L, Baraitser L. Salisbury L, et al. In: Kirtsoglou E, Simpson B, editors. The Time of Anthropology: Studies of Contemporary Chronopolitics. Abingdon: Routledge; 2020. Chapter 5. In: Kirtsoglou E, Simpson B, editors. The Time of Anthropology: Studies of Contemporary Chronopolitics. Abingdon: Routledge; 2020. Chapter 5. PMID: 36137063 Free Books & Documents. Review.
Platelet-rich therapies for musculoskeletal soft tissue injuries.
Moraes VY, Lenza M, Tamaoki MJ, Faloppa F, Belloti JC. Moraes VY, et al. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2014 Apr 29;2014(4):CD010071. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD010071.pub3. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2014. PMID: 24782334 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Peppard PE, Young T, Barnet JH, Palta M, Hagen EW, Hla KM. Increased prevalence of sleep-disordered breathing in adults. Am J Epidemiol. 2013;177(9):1006–14. - PMC - PubMed Heinzer R, Vat S, Marques-Vidal P, Marti-Soler H, Andries D, Tobback N, Mooser V, Preisig M, Malhotra A, Waeber G, et al. Prevalence of sleep-disordered breathing in the general population: the HypnoLaus study. Lancet Respir Med. 2015;3(4):310–8. - PMC - PubMed Tietjens JR, Claman D, Kezirian EJ, De Marco T, Mirzayan A, Sadroonri B, Goldberg AN, Long C, Gerstenfeld EP, Yeghiazarians Y. Obstructive sleep apnea in Cardiovascular Disease: a review of the literature and proposed Multidisciplinary Clinical Management Strategy. J Am Heart Assoc. 2019;8(1):e010440. - PMC - PubMed Malhotra A, White DP. Obstructive sleep apnoea. Lancet. 2002;360(9328):237–45. - PubMed Benjafield AV, Ayas NT, Eastwood PR, Heinzer R, Ip MSM, Morrell MJ, Nunez CM, Patel SR, Penzel T, Pépin JL, et al. Estimation of the global prevalence and burden of obstructive sleep apnoea: a literature-based analysis. Lancet Respir Med. 2019;7(8):687–98. - PMC - PubMedMeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
BioMed Central PubMed CentralMedical
MedlinePlus Health Information相关知识
The Health Benefits of Dietary Fibre
Research progress of correlation between sleep during pregnancy and offspring birth weight
Benefits of Sexual Activity on Psychological, Relational, and Sexual Health During the COVID
The impact of weight self
The Effect of Calorie Tracking on Your Health and Weight Control
impact on the recovery of health guidance on maternal puerperal(影响对孕产妇产后的恢复健康指导).doc
A study on the influencing factors and relative contribution of family on children's health: From the perspective of household production of health
The influence of lifestyle and psychological factors on obesity in an occupational population
System construction of international health impact assessment: From policy to legal status
Metagenomic analysis reveals the signature of gut microbiota associated with human chronotypes
网址: The impact of comprehensive healthy lifestyles on obstructive sleep apnea and the mediating role of BMI: insights from NHANES 2005 https://m.trfsz.com/newsview908673.html
