质膜重塑决定脂肪细胞的扩张和机械适应性
质膜重塑决定脂肪细胞的扩张和机械适应性
IF 14.7 1区 综合性期刊 Q1 MULTIDISCIPLINARY SCIENCES
María C. M. Aboy-Pardal, Marta C. Guadamillas, Carlos R. Guerrero, Mauro Català-Montoro, Mónica Toledano-Donado, Sara Terrés-Domínguez, Dácil M. Pavón, Víctor Jiménez-Jiménez, Daniel Jimenez-Carretero, Moreno Zamai, Cintia Folgueira, Ana Cerezo, Fidel-Nicolás Lolo, Rubén Nogueiras, Guadalupe Sabio, Miguel Sánchez-Álvarez, Asier Echarri, Ricardo Garcia, Miguel A. Del Pozo
摘要
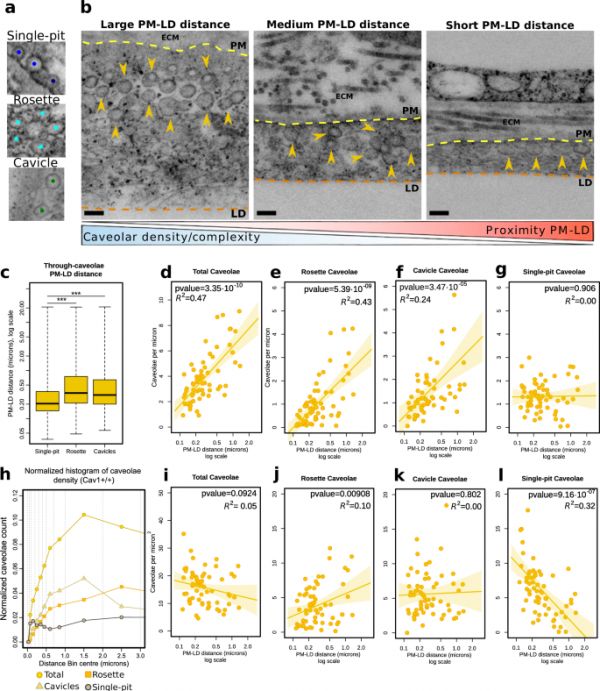
脂肪细胞会大量膨胀,以容纳多余的能量储存,并保护机体免受脂肪毒性的伤害。脂肪组织的可扩张性是肥胖症和脂肪营养不良等疾病的核心;然而,人们对脂肪细胞的生物力学与这些疾病的病因之间的相关性知之甚少。在这里,我们在雄性小鼠体内展示了脂肪细胞质膜在脂滴膨胀时发生的洞穴结构域重组。随着脂滴的增大,洞穴孔会解体以释放其膜储库,增加细胞表面积,并将特定的洞穴孔成分转移到脂滴表面。无洞孔的脂肪组织较硬,变形能力差,在机械挤压下容易破裂。从机理上讲,磷酸化受体 Cav1 Tyr14 是洞穴孔解体所必需的:在该残基上发生 Tyr14Phe 突变的脂肪细胞更硬、更小,导致体内脂肪含量降低;Cav1 和 EHD2 向 LD 表面的转移不足,并显示出不同的 Cav1 分子动力学和张力适应性。这些结果表明,Cav1 磷酸化调控调节洞穴动力学是分化脂肪细胞同态机械适应的相关组成部分。
本文章由计算机程序翻译,如有差异,请以英文原文为准。
Plasma membrane remodeling determines adipocyte expansion and mechanical adaptability
Adipocytes expand massively to accommodate excess energy stores and protect the organism from lipotoxicity. Adipose tissue expandability is at the center of disorders such as obesity and lipodystrophy; however, little is known about the relevance of adipocyte biomechanics on the etiology of these conditions. Here, we show in male mice in vivo that the adipocyte plasma membrane undergoes caveolar domain reorganization upon lipid droplet expansion. As the lipid droplet grows, caveolae disassemble to release their membrane reservoir and increase cell surface area, and transfer specific caveolar components to the LD surface. Adipose tissue null for caveolae is stiffer, shows compromised deformability, and is prone to rupture under mechanical compression. Mechanistically, phosphoacceptor Cav1 Tyr14 is required for caveolae disassembly: adipocytes bearing a Tyr14Phe mutation at this residue are stiffer and smaller, leading to decreased adiposity in vivo; exhibit deficient transfer of Cav1 and EHD2 to the LD surface, and show distinct Cav1 molecular dynamics and tension adaptation. These results indicate that Cav1 phosphoregulation modulates caveolar dynamics as a relevant component of the homeostatic mechanoadaptation of the differentiated adipocyte.
来源期刊

期刊介绍: Nature Communications, an open-access journal, publishes high-quality research spanning all areas of the natural sciences. Papers featured in the journal showcase significant advances relevant to specialists in each respective field. With a 2-year impact factor of 16.6 (2022) and a median time of 8 days from submission to the first editorial decision, Nature Communications is committed to rapid dissemination of research findings. As a multidisciplinary journal, it welcomes contributions from biological, health, physical, chemical, Earth, social, mathematical, applied, and engineering sciences, aiming to highlight important breakthroughs within each domain.
相关文献
二甲双胍通过HDAC6和FoxO3a转录调控肌肉生长抑制素诱导肌肉萎缩
IF 8.9 1区 医学
Min Ju Kang, Ji Wook Moon, Jung Ok Lee, Ji Hae Kim, Eun Jeong Jung, Su Jin Kim, Joo Yeon Oh, Sang Woo Wu, Pu Reum Lee, Sun Hwa Park, Hyeon Soo Kim
具有疾病敏感单倍型的非亲属供体脐带血移植后的1型糖尿病
IF 3.2 3区 医学
Kensuke Matsumoto, Taisuke Matsuyama, Ritsu Sumiyoshi, Matsuo Takuji, Tadashi Yamamoto, Ryosuke Shirasaki, Haruko Tashiro
相关知识
白色脂肪细胞功能障碍...
脂肪组织源性干细胞在临床脂肪雕塑术中的指导意义
Nature Metabolism:脂肪分解:从脂肪储存中动员脂质的细胞机制
脂肪干细胞的基础研究及临床应用
细胞存储(一)——脂肪干细胞
储存脂肪的细胞是什么细胞
什么是脂肪干细胞?
脂肪细胞年轻化定制大师
什么是脂肪干细胞
脂肪活细胞
网址: 质膜重塑决定脂肪细胞的扩张和机械适应性 https://m.trfsz.com/newsview1484846.html