肌营养不良症小鼠模型的药物代谢改变和脂肪肝易感性增加
肌营养不良症小鼠模型的药物代谢改变和脂肪肝易感性增加
IF 15.7 1区 综合性期刊 Q1 MULTIDISCIPLINARY SCIENCES
Zachary Dewald, Oluwafolajimi Adesanya, Haneui Bae, Andrew Gupta, Jessica M. Derham, Ullas V. Chembazhi, Auinash Kalsotra
引用次数: 0
摘要
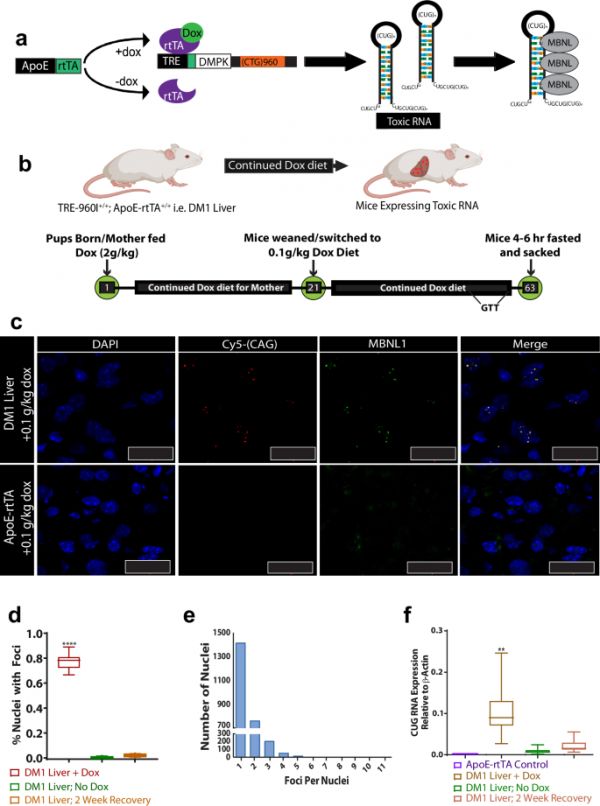
1型肌营养不良症(DM1)是一种高发的肌肉营养不良症,是由DMPK基因中的(CTG)n重复扩增引起的。对DM1的研究主要集中在肌肉和神经组织的影响上;然而,DM1患者也会出现各种代谢和肝脏功能障碍,如对代谢功能障碍相关性脂肪肝(MAFLD)的易感性增加以及对某些药物的敏感性增高。在这里,我们生成了一种肝脏特异性 DM1 小鼠模型,它再现了该疾病的分子和病理特征,包括对 MAFLD 的易感性以及对特定镇痛药和肌肉松弛剂代谢能力的降低。CUG-expanded(CUG)exp重复RNA在肝细胞内的表达封存了肌球蛋白样蛋白,并引发了广泛的基因表达和RNA处理缺陷。从机理上讲,我们证明乙酰-CoA羧化酶1的表达和替代剪接的增加驱动了DM1肝脏中脂质的过度积累,而高脂、高糖饮食又加剧了这种积累。这些发现共同揭示了(CUG)exp RNA毒性会破坏正常的肝功能,使DM1肝脏易受损伤、MAFLD和药物清除病理变化的影响,这些病理变化可能会危及患者的健康并使其治疗复杂化。
本文章由计算机程序翻译,如有差异,请以英文原文为准。
Altered drug metabolism and increased susceptibility to fatty liver disease in a mouse model of myotonic dystrophy
Myotonic Dystrophy type 1 (DM1), a highly prevalent form of muscular dystrophy, is caused by (CTG)n repeat expansion in the DMPK gene. Much of DM1 research has focused on the effects within the muscle and neurological tissues; however, DM1 patients also suffer from various metabolic and liver dysfunctions such as increased susceptibility to metabolic dysfunction-associated fatty liver disease (MAFLD) and heightened sensitivity to certain drugs. Here, we generated a liver-specific DM1 mouse model that reproduces molecular and pathological features of the disease, including susceptibility to MAFLD and reduced capacity to metabolize specific analgesics and muscle relaxants. Expression of CUG-expanded (CUG)exp repeat RNA within hepatocytes sequestered muscleblind-like proteins and triggered widespread gene expression and RNA processing defects. Mechanistically, we demonstrate that increased expression and alternative splicing of acetyl-CoA carboxylase 1 drives excessive lipid accumulation in DM1 livers, which is exacerbated by high-fat, high-sugar diets. Together, these findings reveal that (CUG)exp RNA toxicity disrupts normal hepatic functions, predisposing DM1 livers to injury, MAFLD, and drug clearance pathologies that may jeopardize the health of affected individuals and complicate their treatment.
来源期刊

CiteScore
24.90
自引率
2.40%
发文量
6928
审稿时长
3.7 months
期刊介绍: Nature Communications, an open-access journal, publishes high-quality research spanning all areas of the natural sciences. Papers featured in the journal showcase significant advances relevant to specialists in each respective field. With a 2-year impact factor of 16.6 (2022) and a median time of 8 days from submission to the first editorial decision, Nature Communications is committed to rapid dissemination of research findings. As a multidisciplinary journal, it welcomes contributions from biological, health, physical, chemical, Earth, social, mathematical, applied, and engineering sciences, aiming to highlight important breakthroughs within each domain.
相关文献
二甲双胍通过HDAC6和FoxO3a转录调控肌肉生长抑制素诱导肌肉萎缩
IF 8.9 1区 医学
Min Ju Kang, Ji Wook Moon, Jung Ok Lee, Ji Hae Kim, Eun Jeong Jung, Su Jin Kim, Joo Yeon Oh, Sang Woo Wu, Pu Reum Lee, Sun Hwa Park, Hyeon Soo Kim
具有疾病敏感单倍型的非亲属供体脐带血移植后的1型糖尿病
IF 3.2 3区 医学
Kensuke Matsumoto, Taisuke Matsuyama, Ritsu Sumiyoshi, Matsuo Takuji, Tadashi Yamamoto, Ryosuke Shirasaki, Haruko Tashiro
相关知识
生酮饮食结合运动在改善肥胖小鼠白色脂肪组织质量、血清生物标志物和肝脂代谢的作用
黑木耳子实体粉代替部分膳食对高脂模型小鼠营养性肥胖预防作用
科学网—在高脂肪饮食诱导的肥胖小鼠模型中,运动可防止体重增加并改变肠道微生物群
基于药物代谢组学的肝毒性生物标志物研究进展
专家论坛|核受体在非酒精性脂肪性肝病发病机制和药物开发的应用
营养调控微生物及代谢产物:对免疫和炎症的影响
营养与健康所发现间歇性节食可以改善脂肪肝
局限性脂肪营养不良症状
肝的脂肪代谢
补充杜鹃花醇的高脂肪饮食喂养小鼠肝脏代谢组学和肠道微生物群的特征,Food & Function
网址: 肌营养不良症小鼠模型的药物代谢改变和脂肪肝易感性增加 https://m.trfsz.com/newsview1778679.html
